How to Choose Best DisplayPort Cable: 10 Key Tips
Apr 09, 2025
Leave a message
This article will outline 10 key considerations for choosing the best DisplayPort cables in today's market.
1. Choosing the Best DisplayPort Cable
As video display devices increasingly support 4K and 8K ultra-high-definition resolutions, DisplayPort and HDMI emerge as the leading interface options. DisplayPort interfaces offer greater future scalability, currently supporting 80Gbps maximum bandwidth compared to HDMI's 48Gbps ceiling. Many modern devices incorporate DisplayPort interfaces, which efficiently connect video sources to displays using fewer pins while delivering higher resolutions.
The market offers diverse DisplayPort cable variants (versions 1.2 through 1.4) and form factors (including Mini DisplayPort). How do you choose the best DisplayPort cable? This article breaks down the key considerations for informed selection.
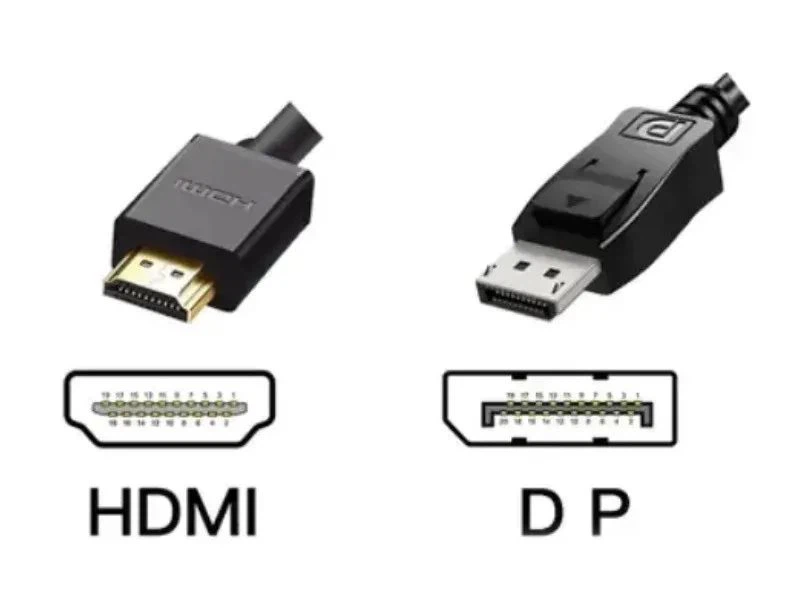

In recent years, the performance of various display devices like TVs and LCD screens has advanced by leaps and bounds. While 4K video devices have begun entering households, 8K ultra-high-definition displays are now targeting the high-end audiovisual market. However, even with high-quality displays and signal sources at home, without matching spec cables, you won't get the most out of your gear. Currently, the widely used HDMI cable requires version 2.1 or above to support 8K (60Hz), but even that only provides 48Gbps bandwidth. If you want high-quality 8K 120Hz ultra-high resolution and frame rate videos, you'll need DisplayPort. DP 2.0 alone supports up to 80Gbps transmission bandwidth and refresh rates up to 240Hz. Especially since most current high-end display devices, graphics cards, and LCD screens mostly come with built-in DisplayPort interfaces, if you need to watch HD movies or play games on your home computer or TV, you'll want to get DisplayPort cables to connect your devices. Different DisplayPort versions support significantly different resolutions and performance levels. Since 8K resolution TVs or LCD screens are still pretty rare in stores, if you're still using Full HD or 4K displays, version 1.2 cables will do the job. For early adopters and those pursuing the ultimate picture quality, they're probably ready to upgrade to 8K resolution TVs and screens, in which case they should go straight for version 1.4 products right away.

2. Evaluating DisplayPort Cable Quality and Manufacturer Expertise
As mentioned in our previous article about DP cables, DP can support a maximum bandwidth of 80Gbps, making it the highest-bandwidth video cable currently available. But to make sure the DP cables you buy actually deliver their advertised bandwidth, the key factor is the cable's quality. Choosing high-quality DP cables ensures stable signal transmission, preventing issues like image distortion or signal dropouts. High-quality cables typically use better materials and design to reduce signal loss and interference.
Here's how to spot a high-quality cable: First, check if the core wire is made of oxygen-free copper. This information can usually be found in official product specs, or you can test it yourself with a multimeter - like we covered in our Ethernet cable article. Pure copper wire should measure about 30 ohms per 100 meters, which cheaper, impure materials often can't match.
Here's what to look for: Also check for multi-layer shielding to ensure the signal stays clean. Take the cable shown below - it uses four shielding layers: two aluminum foil layers, a ground wire, plus a braided aluminum-magnesium mesh.
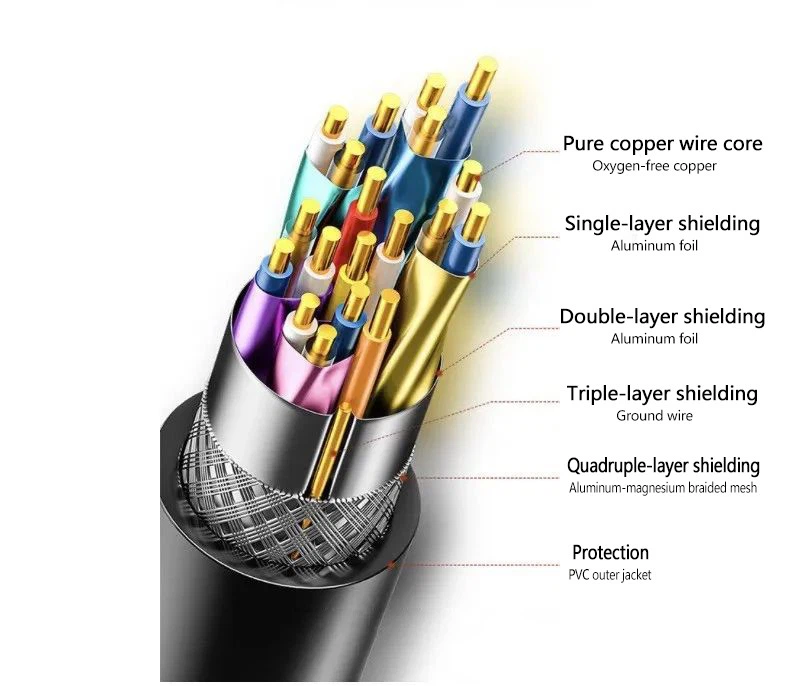
Manufacturing DP cables is a precision craft that demands the highest standards. Only with state-of-the-art equipment, mastery of core technologies, and advanced techniques can a manufacturer deliver premium, defect-free products. You should definitely check the cable company's official website, WeChat, Weibo, and other platforms to verify whether the enterprise invests heavily in both skilled workers and top-notch equipment. Only with top-tier technical specialists and advanced equipment can a company develop robust technical expertise and extensive production experience. Reputable DisplayPort cable manufacturers typically maintain independent production lines featuring complete wire-drawing machines, soldering equipment, and testing devices. What's more, they establish dedicated R&D teams, boasting efficient product development with strong capabilities in intermediate production and final assembly.
3. Understanding Certification Standards of DisplayPort Cables.
Per international HDMI Association standards, only companies authorized by the HDMI Association are permitted to display the HDMI logo on their products and manufacture HDMI cables. Typically, certified companies demonstrate that their technology meets the standards set by the international HDMI organization. When buying HDMI cables, it's crucial to choose products from HDMI Association-certified companies!
VESA has decided to certify and label DP 2.0 cables to differentiate between different speed ratings. Specifically, DP 2.0 cables have two standards: DP40 and DP80. DP40 cables use the UHBR10 standard, delivering 10Gbps per lane across four channels for a total bandwidth of 40Gbps, while DP80 cables adhere to the UHBR20 standard with 20Gbps per lane, totaling 80Gbps. This certification ensures cable performance and quality, preventing market confusion and false claims.
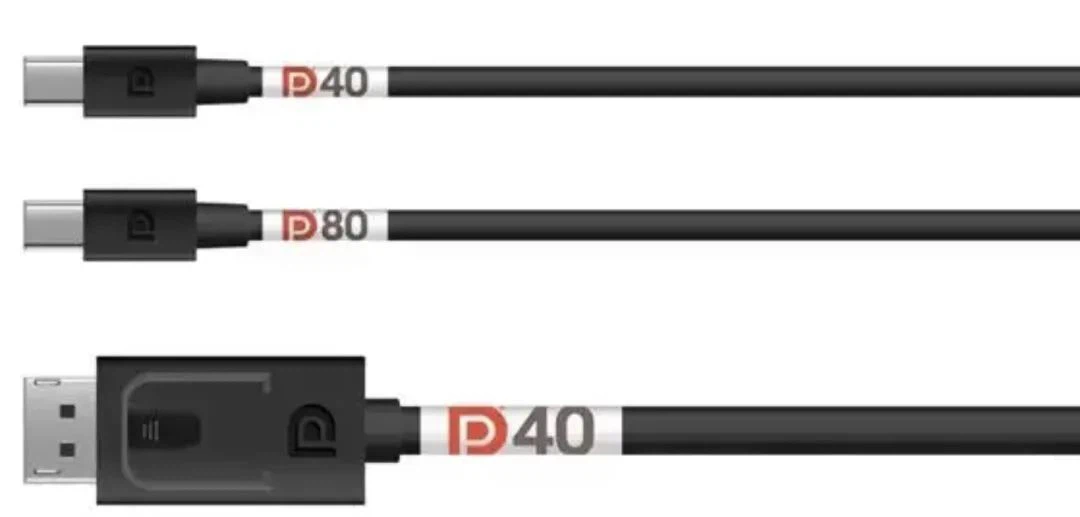

For certification, products must first pass testing at a DisplayPort ATC (Authorized Test Center), then submit results to VESA for review. Certified products can then execute a License Agreement to use the DisplayPort certification logo and have their product information listed on the DisplayPort website. The DisplayPort certification program is open to non-member companies too, but non-members must pay a USD 1,500 annual licensing fee to gain rights to use the certification logo.

4. wire Core Materials and Shielding Layer of DisplayPort Cables.
We covered some aspects of DP video cable quality in our last article. The copper used in DP cables is primarily OFC (oxygen-free copper), and few manufacturers produce DP cables with inferior cores, mainly because DP cables are currently used in professional high-end display markets. Cheap DP cables can't reliably handle 4K UHD and are easily detected during testing.
Currently, DP cables come in two core types: copper and fiber-optic. Copper-core DP cables mainly use OFC(Oxygen-free Copper), delivering stable, plug-and-play performance and high cost-effectiveness, making them market favorites. However, due to material limitations, they're typically suited for short-distance scenarios within 10 meters. Over longer distances, they face serious signal loss, interference susceptibility, and poor image quality, failing to meet high-bandwidth demands.
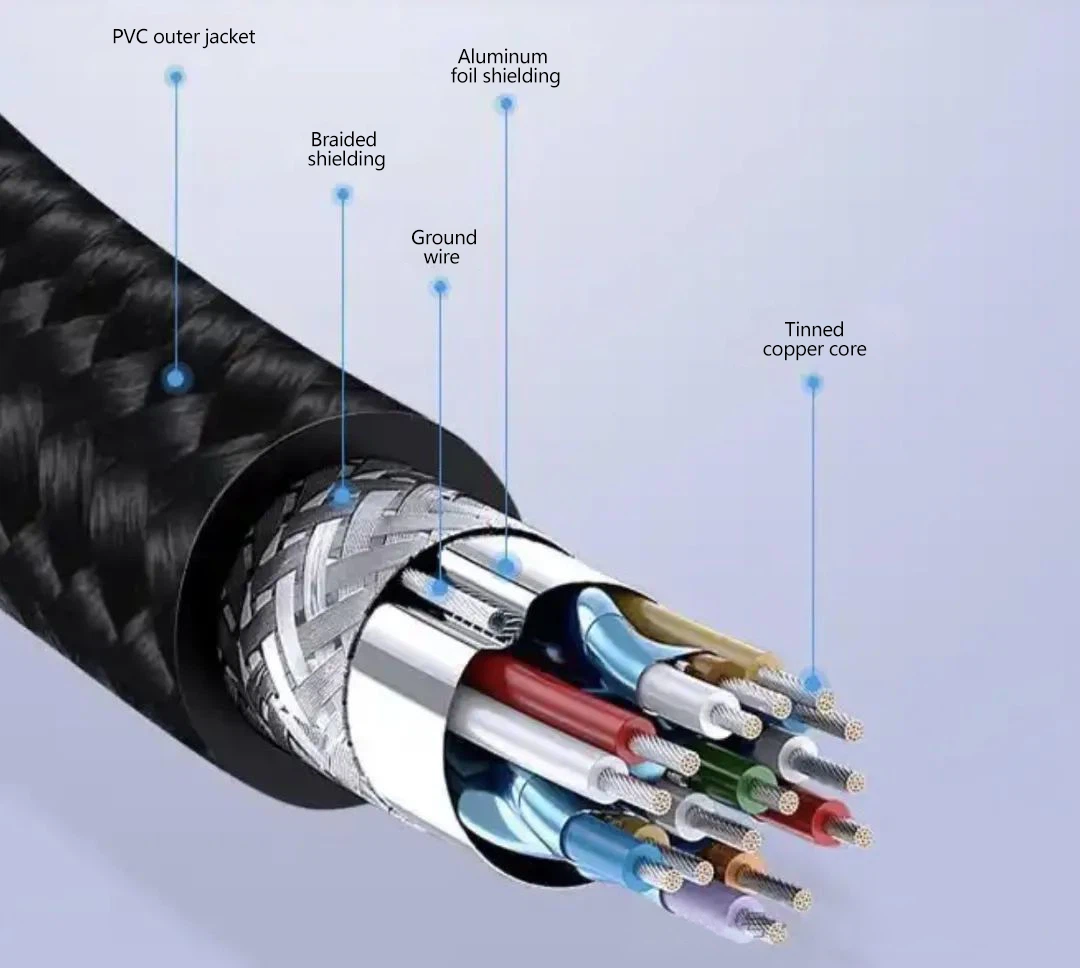
Fiber-optic DP cables feature built-in electro-optical conversion chips, using light signals that enable unlimited high-bandwidth transmission. They're completely immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI), with ranges exceeding 100 meters-the key reason for their premium pricing. Major e-commerce platforms show fiber-optic DP cables (1-10m) priced at 300-600 RMB (~$40-85), costing 5-10x more than copper-core cables (under 200 RMB).
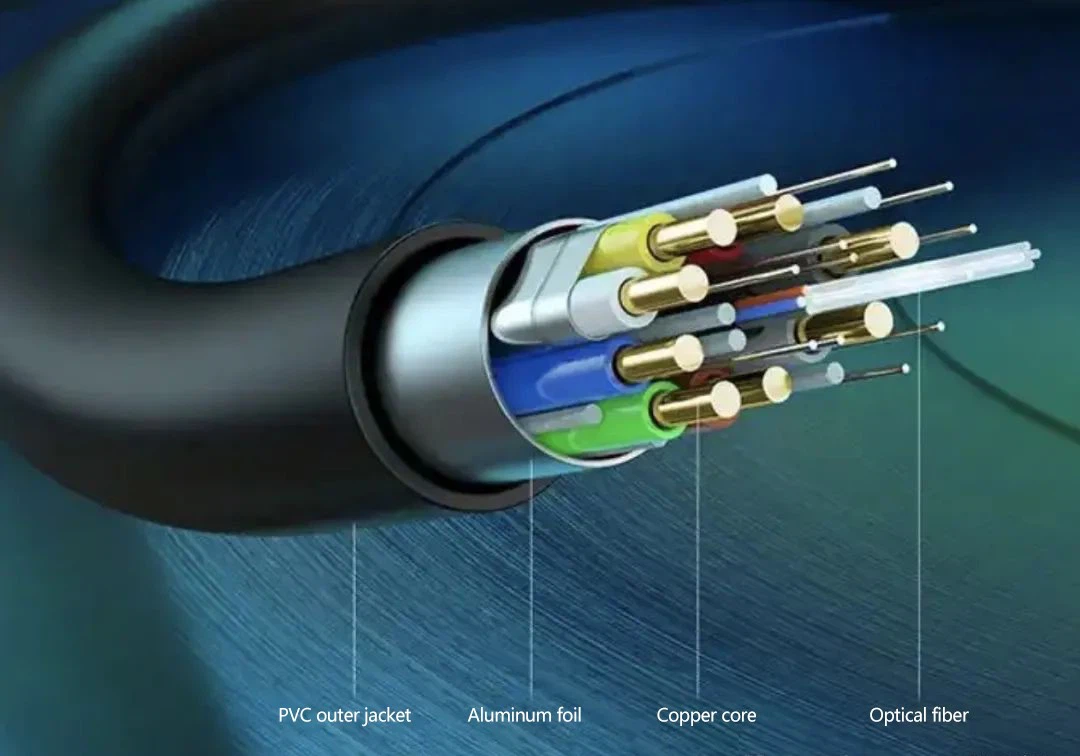
Pro tip: Fiber-optic DP cables are unidirectional (marked Source → Display)-you must connect them correctly, as reversed connections won't display.
DP cable performance also depends heavily on shielding layers, which prevent internal/external signal interference from degrading AV quality. Shielding effectiveness correlates with material coverage density-higher density means better protection. Typically, DP cables have 85% metal braid coverage. The aluminum foil layer achieves 100% coverage.
5. Outer Jacket Durability of DisplayPort Cables
A high-quality DP outer jacket is tough as nails and requires considerable effort to dismantle-it cannot be torn by hand and requires wire cutters or heavy-duty scissors. Meanwhile, PVC jackets made from recycled materials tear apart easily by hand. After cutting through the first layer of PVC shielding, a dense and highly durable aluminum-magnesium alloy shield is revealed, which similarly demands wire cutters. The final layer is an aluminum foil shield.
Common DP cable outer jacket materials: PVC and nylon braiding.
PVC Jacket: The Go-To for Wear and Tear Resistance
The PVC jacket uses amorphous material, excelling in oxidation, strong acid, and reduction resistance. DP cables with PVC jackets resist wear, stretching, and aging, delivering high strength and stability. Whether for daily use or long-term connections, the jacket holds up reliably.
The PVC jacket uses amorphous material, excelling in oxidation, strong acid, and reduction resistance. DP cables with PVC jackets resist wear, stretching, and aging, delivering high strength and stability. Whether for daily use or long-term connections, the jacket holds up reliably.

Nylon Braided Jacket: Enhanced Toughness and Tensile Strength
High-quality DisplayPort cables feature a nylon braided jacket, protecting internal wiring while boosting performance. Snag-resistant and heavy-duty, these cables resist wear and fraying-built to last.
High-quality DisplayPort cables feature a nylon braided jacket, protecting internal wiring while boosting performance. Snag-resistant and heavy-duty, these cables resist wear and fraying-built to last.
6. AWG Gauge & Length Tips of DisplayPort Cables
When shopping for DP cables, you'll notice many products highlight their conductors follow AWG gauges, like 26AWG or 24AWG gauges, with some even marked as "24AWG" on the cable jacket. We've previously explained AWG cables in our Ethernet cable and HDMI cable guides-interested readers can search our official account for details.
The AWG number (e.g., 24AWG or 26AWG) refers to the wire gauge size determined during manufacturing. Here's the crucial part: bigger AWG number means thinner wire-it's counterintuitive! Just remember: the higher the number, the smaller the diameter.

Another key factor is cable length. 8K ultra-HD video requires huge data throughput, and longer cables suffer greater signal loss. While professional-grade fiber optic DP cables exist, they're pricey without delivering noticeably better performance. Measure your setup's cable runs first and aim for under 10 meters where possible. Beyond 10 meters, fiber optic versions might be your only option.
Here's the thing: while shorter cables reduce signal degradation, cutting it too close length-wise might put strain when connecting or moving devices, risking internal wire damage. Leave some slack during installation-it gives you wiggle room and prevents yanking on the cable.
7. Understanding DP Interface Versions of DisplayPort cables.
We've covered DP cable and interface versions before, from DP1.0 to DP2.1, with each version improving bandwidth, resolution, and refresh rate. For example, DP1.4 supports 4K at 120Hz or 8K at 60Hz, while DP2.0 can handle resolutions up to 16K with higher refresh rates than DP1.4. You might think, "I should just get DP2.1 for compatibility," but DP2.1 cables cost about triple DP1.4 cables.
Checking major online stores, DP2.1 cables cost around 300 yuan, while DP1.4 cables run about 130 yuan.
So what should you choose? Just get what you need - don't waste money on high-end specs. Consider your device's interface version - if it only supports DP1.4, buying a DP2.0 or DP2.1 cable won't give you any real advantage, yet costs much more.
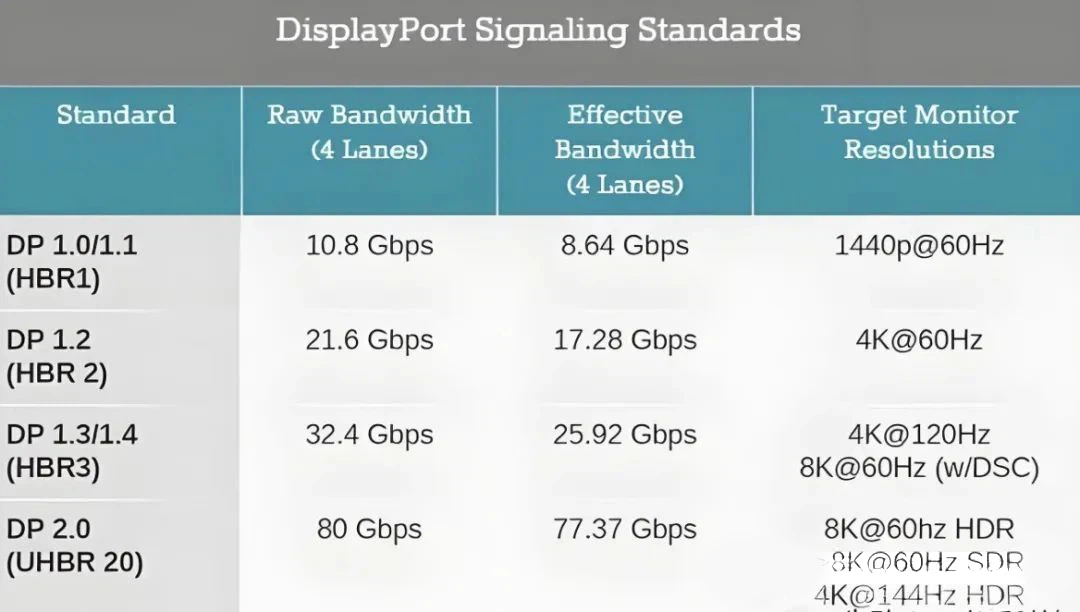
Also think about what the signal you'll need in the future. If you're using HD now and expect basic 4K with high frame rates in 3-5 years, DP1.4 will do just fine at a lower price. For research labs or special projects needing higher bandwidth and resolution, DP2.0 or DP2.1 might make sense - just remember DP2.1 cables cost way more.
8. Identifying DP Interface Types of DisplayPort cables - Physical Design.
Our previous article covered the two types of DP interfaces: DP and Mini DP. Before buying a DP cable, make sure to check what kind of DP port your display has.

DP and Mini DP ports look very different in size, so pay attention when choosing. Always double-check if you need DP, Mini DP, or Thunderbolt. We now know that Mini DP and Thunderbolt ports share the same physical dimensions, but their features aren't exactly the same. So, this might not seem like a big deal, but you should always check your device's port type before buying.

9. Evaluating DP Connector Build Quality of DisplayPort cables
If a DP cable's connector is gold-plated, it's not just more attractive - it also has high corrosion resistance, excellent conductivity, is easy to solder, heat-resistant, and has good wear resistance. That's why gold-plated connectors are better than non-gold-plated ones, though more expensive. Most gold-plated connectors on the market use 24K gold, which gives them a brighter appearance. But a gold-plated DP connector doesn't always mean better image quality, because what actually connects to the device's DP port are the PIN needles inside. So the PIN needles' conductivity and wear resistance are very important.
These PIN needles are typically made of tin bronze, which has high elasticity, excellent wear and corrosion resistance. Usually, they're first nickel-plated before being gold-plated, so a well-made DP cable's PIN needles will show three distinct layers.

For the outer shell, most cables use plastic while higher-end models use aluminum or zinc alloy. This doesn't affect actual transmission performance, but the metal ones look better and last longer with frequent use.

10. Applications of DP++ in DisplayPort cables
DP++ (DisplayPort++), also called DisplayPort Dual Mode, mainly boosts the DisplayPort interface's compatibility and flexibility. The DP++ interface not only handles DisplayPort standard signals but can also convert and work with DVI and HDMI signals. Using built-in conversion circuits or the right adapters, DisplayPort++ transforms DisplayPort signals into DVI or HDMI, greatly improving the interface's versatility.

So when would you use DP++ interfaces and cables? First, when you need compatibility with multiple video output protocols: DP++ supports DisplayPort, DVI, and HDMI, so it can work with different display devices without interface limitations. Second, DP++ makes connecting devices more flexible: if you need to hook up several displays or switch devices, the DP++ interface offers an easier solution.






