What are Cat 6 Cables?
May 23, 2024
Leave a message
Do you realy know what is a Cat6 cable? Cat 6 Cables or Cat6 twisted pair cables are divided into unshielded twisted pair (6E) and shielded twisted pair (6EA). The core of Cat 6 cables consists of bare copper conductors of either 23AWG or 24AWG.
1. Introduction to Cat 6 Standards
The Cat 6 Cable (UTP) cabling standard will be the ultimate standard for future UTP cabling and, while providing a basis for selecting higher-performing products for users, it should also meet the requirements of network application standards organizations. It is mainly used for 100-megabit, gigabit, 10-gigabit, and 100-gigabit Ethernet technologies in medium to large companies. The specifications in Cat 6 standards involve media, cabling distances, interface types, topology structure, installation practices, channel performance, and the performance requirements for cables and connecting hardwares.
Cat 6 standards specify the highest performance that copper cable systems should provide, allowing the use of UTP or STP cables and connecting types; the entire system, including applications and interface types, must be backward compatible, meaning that applications running on Cat 3 or 5 systems should also operate on the new Cat 6 systems, and the user interface should use 8-position modular jacks. Like Cat 5 standards, the Cat 6 cabling standards also adopt a star topology, with cabling distance requirements stating that the length of the basic link (permanent link) must not exceed 90 meters, and the channel length must not exceed 100 meters.
Cat 6 cables and systems should have a frequency range of 1~250MHz. The cable system,hardwares, basic links, and channels at all frequency points are required to test the following parameters:
□ Attenuation
□ Return Loss
□ Delay/Skew
□ Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT)
□ Powersum Near-End Crosstalk (Powersum NEXT)
□ Equal Level Far-End Crosstalk (ELFEXT)
□ Powersum Equal Level Far-End Crosstalk (Powersum ELFEXT)
□ Balance (LCL, LCTL)
□ Others
Additionally, the testing environment should be set under worst-case scenarios, testing both products and systems to ensure the usability of the test results. The provided test results should also represent the worst-case values rather than average values.
At the same time, Cat 6 is a comprehensive specification and can receive support in the following areas:
□ Laboratory testing procedures
□ Field testing requirements
□ Installation practices
□ Other considerations regarding flexibility and longevity
2. Cat 6 Cabling
The Cat 6 cabling system was developed based on research from T1A TR41. The purpose of the standard is to implement gigabit solutions. The gigabit schemes were originally devised based on Cat 5 cabling systems, and using Cat 6 could reduce costs by half compared to the Cat 5E. The Cat 6 parameter margins can better meet the needs of gigabit schemes.
3. Physical Structure of Cat 6 Twisted Pair
Cat 6 twisted pair cables have certain differences in appearance and structure from Cat 5 or Cat 5E twisted pair cables. They come in two physical structures.
(1) Insulated Cross Skeleton
Not only does the physical structure of the Cat 6 twisted pair cable add an insulated cross skeleton, which places each pair of twisted wires into the four grooves of the cross skeleton, but the diameter of the cable is also thicker. The cross skeleton in the center of the cable rotates with changing lengths, securing the four pairs of twisted wires into the skeleton's grooves, maintaining the relative positions of the four pairs and improving the cable's balance characteristics and crosstalk attenuation. The physical structure with the insulated cross skeleton for Cat 6 twisted pair cables is shown in Figure 1.
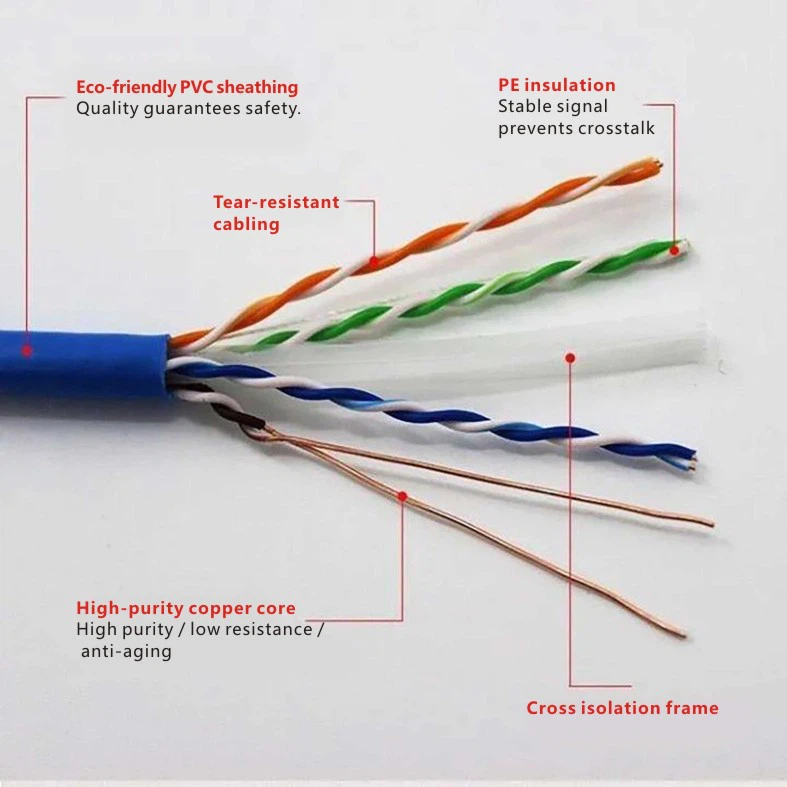
Figure 1: Physical Structure of Cat 6 Cross Skeleton Twisted Pair
(2) Flat Cat 6 Twisted Pair
The physical structure of the flat Cat 6 twisted pair cable is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Physical Structure of Flat Cat 6 Twisted Pair
4. Performance Indicators of Cat 6 Cabling
The performance indicators for Cat 6 cabling products given by ISO/IEC are shown in Table 1.

Key issues for cabling standards:
□ At 250MHz, Cat 6 channels must provide a positive (+ve) PSACR value (0..1dB).
□ Cat 6 channels include links with 2, 3, or 4 joints link.
□ The defined frequency values for Cat 6 channels, not field frequency values, are 250MHz. The bandwidth was boosted to 250MHz to meet the requirement of a zero ACR value as defined by the IEEE802 committee in new cabling standards, thereby increasing the frequency by 25%.
□ Performance parameters for cables and components need to be recalculated from the channel system.
□ Cat 6 components should have interoperability-allowing the use of different manufacturers' products in combination.
□ Cat 6 components should be backward compatible with Cat 5 and enhanced Cat 5 features.
The last two points will bring more competition to connector manufacturers. However, the loop loss issue for Cat 6 systems has not been entirely resolved, and performance indicators for cables and connectors need further improvement. Loop loss is a very important system performance parameter. The EIA/TIA subcommittee proposed in Appendix 5 of 568A (5e) to adopt stricter connector and cable loop loss levels to ensure compliance with system-defined level requirements, and likewise, Cat 6 systems have added more requirements than Cat 5e.
5. Performance Indicators for 23AWG Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable of Cat 6, 4-Pair Twisted Pair
Cat 6, 4-pair twisted pair uses 23AWG solid bare copper conductors, with ethylene propylene fluoride as the insulation material, and has a transmission frequency of up to 350MHz.
The performance indicators for the Cat 6, 4-pair, 23AWG unshielded twisted pair cable are shown in Table 2 below.
| Frequency (MHz) | Near-End Crosstalk (dB) | Attenuation (dB) | ACR (dB) | Echo Loss (dB) | ELFEXT (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.0 | 1.6 | 82.4 | 24.5 | 77.7 |
| 4 | 70.8 | 3.3 | 67.3 | 25.5 | 65.1 |
| 8 | 65.8 | 4.2 | 61.6 | 25.9 | 58.9 |
| 10 | 63.7 | 5.3 | 61.4 | 26.1 | 57.3 |
| 16 | 61.5 | 6.7 | 53.8 | 26.2 | 53.7 |
| 20 | 58.5 | 7.5 | 51.0 | 28.2 | 52.2 |
| 25 | 58.0 | 8.6 | 49.4 | 29.0 | 50.2 |
| 31 | 56.0 | 9.7 | 46.3 | 27.9 | 49.1 |
| 63 | 52.8 | 143 | 38.5 | 25.9 | 48.3 |
| 100 | 51.2 | 18.5 | 32.7 | 23.7 | 40.3 |
| 155 | 47.5 | 22.9 | 24.6 | 21.2 | 39.4 |
| 200 | 49.5 | 26.7 | 22.6 | 20.1 | 36.5 |
| 250 | 44.8 | 29.7 | 15.1 | 19.1 | 33.0 |
| 300 | 42.8 | 32.6 | 10.2 | 18.2 | 30.7 |
| 350 | 40.4 | 35.8 | 7.6 | 17.2 | 23.6 |
Previous:What Are Network Cables?
Next:What is Cat7 Cable?






